IoT is bringing revolution to almost every aspect of our lives by changing how we do things. The use of Smart IoT devices is on the rise with all the industries heavily investing in IoT. The main aims of investing in IoT are to improve operations efficiency, improve product quality, and reduce the costs of production. The Agricultural industry is among the industries seeking to reap the benefits of IoT. The use of IoT in agriculture is commonly referred to as Smart Farming or Smart Agriculture. It uses various IoT sensors to send the farm’s data, like humidity, temperature, soil moisture, etc. to the cloud which can be monitored and controlled from anywhere in the world.
According to the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO), there will be eight billion people globally by the year 2025 and 9.6 billion by 2050. This means that food production must go up by 70 percent to feed that population. IoT is one of the technologies expected to assist in reaching that goal.
How IoT is implemented in Agriculture
There are several ways of implementing Smart Agriculture using IoT
- Precision Farming
- Agricultural Drones
- Livestock Monitoring
- Smart Greenhouses
1. Precision Farming
Precision farming is the most famous application of smart farming using IoT. Precision farming is the practice of making agricultural processes more accurate and controlled for rearing livestock and crop growing. The main components of precision farming are the IT systems, sensors, control systems, automated hardware, and autonomous vehicles, among others. IoT introduces the idea of connecting these systems and devices using the internet for better data storage and analytics. IoT improves services such as livestock monitoring, soil moisture probes, inventory monitoring, and tracking of vehicles, among others. Precision farming involves the collection of data through sensors and analyzing it for use by farmers to make informed and quick decisions.
2. Agricultural Drones

Drones are being used to improve several agricultural practices in Smart Farming Using IoT. There are two types of agricultural drones, the surface-based and aerial-based. The drones are used for activities such as assessment of crop health, spraying of crops, planting, soil and field analysis, crop monitoring, and irrigation.
Drones can collect multispectral, thermal and visual imagery data that provide the farmers with a wide array of metrics such as plant health, plant count and expected yield, soil nitrogen and moisture content, drainage mapping, and canopy cover mapping. The data helps the farmer make the right decisions and use only the required resources to avoid wastage.
Aerial drones cover more land than a ground-based human observer in the same amount of time as it has the ability to avoid barriers. Automating drones to carry out routine assessments eliminates the need for human operation. The drones are deployed to cover large tracts of land where regular monitoring is required. Also, drones are very useful in situations where bacteria, fungus, or pests are difficult to control and require regular spraying and monitoring.
3. Livestock Monitoring
Livestock monitoring is also become ‘Smart’ in smart agriculture using IoT. It enables farmers to monitor the condition of their animals. The farmer can monitor the animals’ activities such as movements, eating habits, weight, and reproductive cycle, among others.
The IoT solutions for livestock monitoring involves animal wearables that connect to a gateway using a low-cost and low bandwidth technology (LoRaWAN) to transmit data to the cloud. The wearables contain sensors that monitor aspects such as blood pressure, respiration, heart rate, body temperature, and digestion, among others. The data is used in decision making and keeping the health in check. The farmers are able to take corrective measures well in time. For instance, they are able to identify a sick animal and call a veterinary doctor well in time to prevent death or spread the disease to other animals. Reproductive cycles and calving are monitored by collecting data relating to time on heat, and the time to give birth.
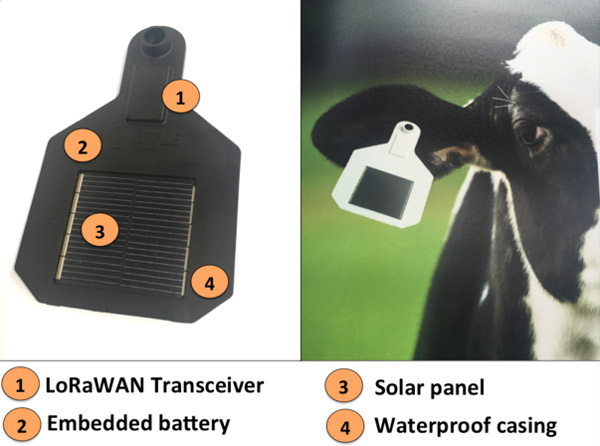
An example of an IoT livestock monitoring device is the Cattle Traxx. This device contains battery-and-solar-charged sensors which transmit data using LoRaWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network). The sensors on the cow form a mesh network to enable efficient data collection. Cattle Traxx collects data regarding animal health using the sensors, and location details using Geofencing.
4. Smart Greenhouses

Traditional greenhouses relied on manual interventions to control environmental parameters for the growth of crops. However, manual interventions have disadvantages such as energy loss and production loss. Smart greenhouse solves these issues by use of IoT systems by monitoring and controlling aspects such as temperatures, luminosity, soil and mineral content, and humidity. Using the collected data, optimal plant growth conditions can be maintained to ensure maximum production. The actuators are controlled automatically to control the conditions by performing actions like opening a window, turning on the lights, and controlling the heater and fan, among others.
Smart greenhouses also help in reducing wastage smart agriculture using IOT. By monitoring moisture content, the right amount of water can be used for irrigation and this prevents wastage, the same case applies to soil mineral content as the right minerals in the right amounts are used. This reduces wastage and maintains a balance that is best for crop growth.
Benefits of IoT Applications in Agriculture
Several benefits arise from the application of IoT in Agriculture. IoT application leads to Increase production in crops and livestock through creating the right environment, monitoring and controlling different aspects. Secondly, IoT helps in reducing the cost of production, especially in largescale farming. The IoT devices reduce the need for human interventions, thus reducing the number of employees on a farm. Additionally, the IoT application reduces the wastage of resources such as water, fertilizers, and machine spare parts. They ensure only the right amounts of water and minerals are added to the soil. Sensors on vehicles and agricultural machines aid in predictive maintenance to ensure timely repairs and only the faulty parts are replaced. Lastly, the application of IoT improves overall farm operational efficiencies by providing data that allows every process to run optimally.
Conclusion - Smart Farming using IoT
So after knowing about some IoT applications in agriculture, we can say that it is definitely revolutionize the agriculture industry in a few years. IoT has been applied in several areas of agriculture. A lot of research is underway to ensure more IoT devices are used to make the managing of farms easier and increase productivity. IoT is allowing farmers to easily obtain data that is useful in many ways such as decision making. With the increasing demand for food due to the rapid population increase, we expect more IoT applications in the next few years.















