Internet of Things (IoT) was among the technologies alien for most countries in the world, however, its penetration has increased to a whole new extent, giving rise to the development of ‘intelligent’ and ‘smart’ devices. As convenience and efficiency are becoming a priority in most applications, the integration of IoT will boost innovation more than ever in the coming year.
In most practical applications of IoT, the heart of the circuit includes a microcontroller, a temperature sensor, a communication protocol, and a power supply. With the recent advancements in sensor technology, designing more circuits for more precise applications has become possible.
This article discusses the top IoT applications that will enjoy immense success in 2020, and about the basic electronic components/modules used with IoT that are integrated into these circuits. The article gives real-time examples of state-of-the-art AI applications and innovations launched by market leaders, indicating the emerging trends in the landscape.
1. Smart Health Monitoring Device
Healthcare is one of the biggest industries to have adopted next-generation technologies for developing state-of-the-art medical devices. Taking into consideration the importance of accuracy and real-time monitoring of various attributes such as heart rate, body temperature, and heart rate variability, the need for connecting patient monitoring devices with the IoT protocol will soon be inevitable.
Developing an IoT-enabled, smart health monitoring system involves a microcontroller, and that of the Arduino series is gaining popularity among developers. Arduino Pro Mini is the smallest controller of the Arduino series and is preferred in a variety of battery-operated, portable health monitoring devices. Microcontroller ESP8266, which is a Wi-Fi-based microcontroller, is another component commonly used in designing smart health monitoring devices.

Dubai Health Authority (DHA) – a government organization overseeing the health system of Dubai, United Arab Emirates – recently announced that it will soon launch AI-based solutions for improving health care delivery systems, by collaborating with six companies. The new products will include features such as smart home care solutions, eye disease detection in diabetic patients, and wearable technology for quick and smart analysis of body vitals.
2. Smart Fitness Trackers
The increasing rise of the health & wellness wave has been triggering consumers to keep track of their fitness regimes through state-of-the-art consumer electronics and IoT-enabled wearable. Connected fitness bands or smart shoes with body sensors and connectivity through a smartphone are gaining immense popularity among health-conscious consumers. Smart fitness tracker devices and IoT-based fitness wearables can be designed using various IoT sensors such as accelerometer sensors, ultraviolet sensors, ambient light sensors, skin response sensors, and bioimpedance sensors. Though the design of these circuits can be significantly similar to smart health monitoring devices, their portable nature can influence the choice of electronic components that lay the foundation of the circuit for smart fitness bands or smart shoes.
![]()
Amazon had recently announced that it may soon launch Alexa-enabled smart fitness-tracking wireless earbuds that can track various fitness parameters such as the number of calories burnt, distance and pace of running, among others. Xiaomi also recently launched the launch of its latest Hey+ 1S fitness tracker, which has a 120mAh battery and runs on HeyOS, Xiaomi's custom operating system.
3. Smart Home
Connected homes are no longer a concept from the future; the ubiquity of intelligent, voice-controlled devices makes smart homes and IoT home automation mainstream. Developing an IoT-based home automation system with a PIC microcontroller is gaining immense popularity among beginners. PIC16F877 offers the advantages of the combination of CMOS and RISC architecture and makes programming easy for the developers. With the use of these microcontrollers, in combination with sensors, a smart home automation system can be designed which enables operating various appliances remotely, simply using the internet.

A leading Canadian manufacturer of smart home devices – Sinopé Technologies recently launched its new smart home ecosystem which includes smart thermostats, a smart water damage protection system, and a smart plug and wall outlet to control and adjust accent lighting, which can be operated through the Neviweb app.
4. Smart Refrigerator
With the increasing popularity of the application of IoT in smart or connected homes, consumers are willing to integrate the technology with various types of home appliances such as washing machines, air conditioners, security systems, and gas/fire detection systems. However, a smart refrigerator is one of the most popular applications of IoT.
A low-cost smart refrigeration prototype can be designed using Raspberry Pi, multiple sensors including a gas sensor and a camera such as ESP32-cam module which is a Wi-Fi-based Pi camera, load cell, and connecting the whole system to a smartphone application. The camera maintains real-time footage of the food products kept in the refrigerator and detects the expiry of those products, which ultimately saves money and food wastage.
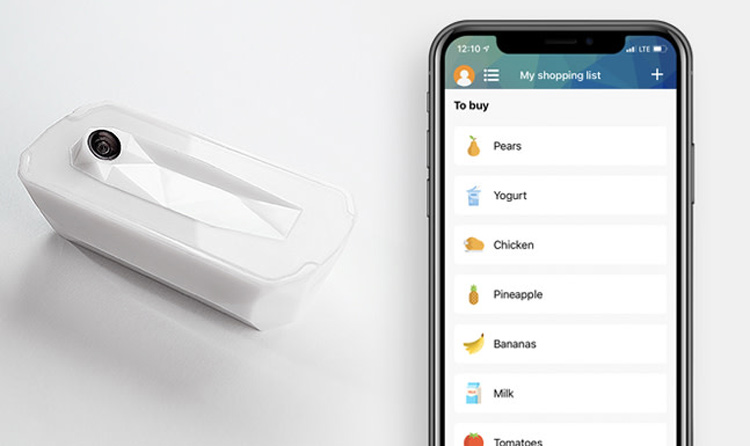
brezzl. GmbH – an innovation company and a design agency headquartered in Munich – recently announced the launch of its Indiegogo campaign in order to fund the production of “Fridge Eye”, which is a smart refrigerator integrated with a rechargeable (via USB-C) camera and an AI system that can operate as a food manager inside the refrigerator.
5. Smart Locks/Connected Home Security
While consumers are showing a proclivity towards transitioning their conventional home appliances into ‘smart’ ones, IoT home security remains the most important concern for them, and this makes smart locks or smart home security systems one of the most popular applications of IoT. Despite the growing awareness about potential cyber-attacks and cyber threats to IoT-enabled security systems, it is only considered a way of strengthening home security using these advanced technologies.
Designing a smart lock that can be operated using Bluetooth, internet, or just a smartphone is simple. It requires a microcontroller, an Arduino UNO in this case, a servo motor, biometric readers, multiple sensors, and a power supply. However, the modern developers are shifting to Raspberry Pi from Arduino, to leverage the stronger and faster processor, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capacity, and simple installation programs of the prior.

Level Home – a smart home start-up – recently announced that it has collaborated with Walmart and a construction company – Lennar Homes, to introduce an ‘invisible’ smart lock with a body camera. The company also announced that the lock is intuitive and can be operated through smartphones by establishing an encrypted connection.
6. Smart Cars
While the houses are on the verge of getting smarter than ever, cars and other automobiles are no exception either. Various controls and operations in a vehicle can be carried out using intelligent technologies. Smart cars with features like real-time telematics tracking, speed control, location tracking, and scheduling, smart infotainment, and smart parking systems are some promising fields. IoT can be implemented in cars using a microcontroller and a communication protocol to carry of derived operations in a vehicle. Arduino integrated development environment (IDE) is used vastly in speed control and obstacle detection applications in smart cars.

Tesla, a leading and one of the very few players in the smart car industry, recently declared that it is rolling out a new software update – Smart Summons – for its cars. The company announced that the new software update is one of the most advanced semi-driving features in smart cars that Tesla has ever launched so far. This new feature can automatically drive the car through a parking area to collect an available parking lot.
7. Connected Factory
As the industrial landscape is undergoing its fourth revolution – Industry 4.0, factory automation has become an indispensable part of the manufacturing industry. A basic design of a smart, connected factory includes a control system consisting of a microcontroller, input/output sensors, and an actuator. As a distributed control system (DCS), a programmable logic controller (PLC), or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems make the fundamental system in most industrial processes, designing an automated factory can prove to be complex, especially for small-scale factories.
Deloitte, a leading consulting and advisory service provider, announced that it has entered the smart factory landscape with the launch of a pre-configured suite of a cloud-based Internet of Things (IoT) applications – Smart Factory Fabric. The new software is powered by Amazon Web Services and it can implement analytics across a connected factory to optimize real-time operations, workforce management, as well as implementation and navigation of various tech-driven smart equipment.
8. Smart Retail
With the retail industry making a move towards adopting innovative technologies to undergo digital transformation, IoT is being integrated into a mounting number of devices, boosting the popularity of smart shopping trolley, smart cart, smart barcode reader, and automatic billing system. Despite the increasing growth of the eCommerce industry, the scope for automation in retail operations is paramount.
Smart barcode readers are being incorporated vastly in shopping carts and trolleys to eliminate the need to stand in long queues for billing. Arduino Mega 2560 or ATMEGA328 are among the popular choices of microcontrollers used in smart barcode readers in combination with RFID tags and readers, a Wi-Fi module, and a power supply.
9. Smart Infant Monitor
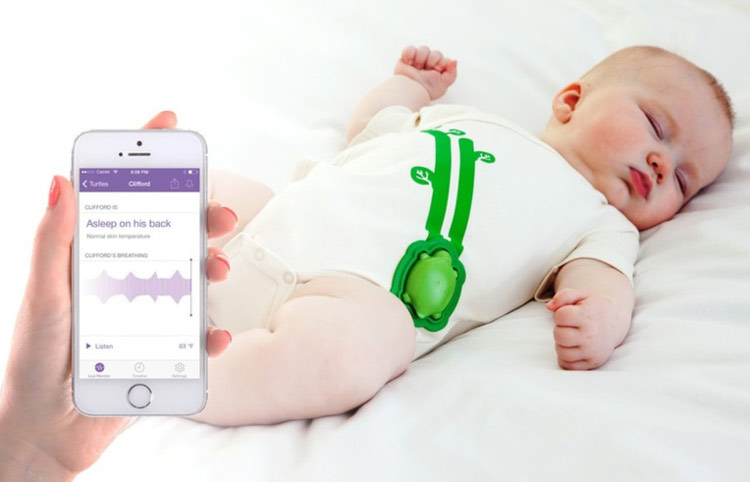

Infant monitors are among the most basic types of communication devices, however, with the increasing concerns over baby’s safety are triggering the integration of advanced technologies that enable parents to monitor the actions of their baby remotely and 24x7. IoT-enabled baby monitors are not only integrated with cameras and other sensors that carry out cry detection mechanism, but also consist of a DC motor that swings the cradle once the baby starts crying.
IoT-based cradle monitoring systems can be designed using a Node microcontroller (ESP8266), sensors including sound sensors, temperature, and humidity sensors, and motion sensors, a DC motor, and an IoT-based server. Integrating cameras for live surveillance while connecting the whole circuit to cloud computing can also be possible by using Raspberry Pi, which makes operating the smart cradle monitor intelligently and remotely much easier.
A next-generation mobile app was recently launched by researchers at the University of Washington to connect speaker devices such as Echo by Amazon to infant monitoring systems itotrack baby’s breathing and diagnose symptoms for sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
10. Smart Farming
Agriculture is one of the biggest industries in most countries, especially in India, yet it remains far from the touch of automation technologies and IoT. Although, it is not rocket science to automate various farming or gardening activities through IoT. A smart gardening/farming system that can be controlled using a smartphone can be prototyped with the use of Raspberry Pi3 Model B, temperature and moisture sensors, luminosity sensors, and a power supply.
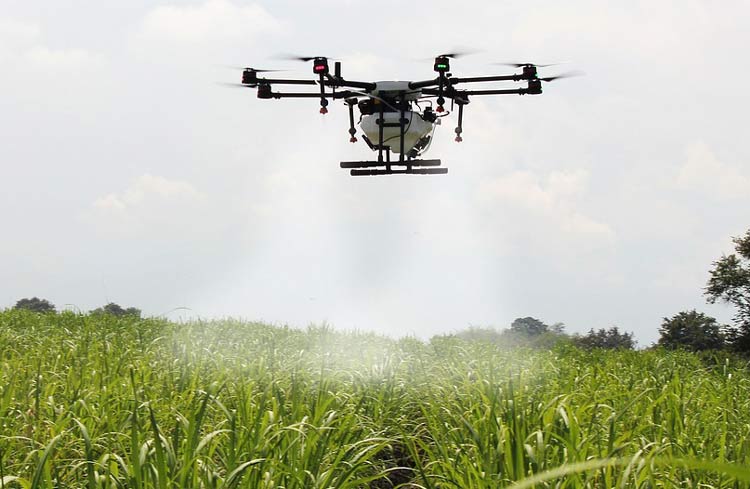

Many Western countries are encouraging farmers to automate various farming operations, such as irrigation, through IoT to further enhance productivity and farming efficiency. A simple circuit of a basic smart irrigation system includes a microcontroller, water pump, moisture sensor, relay, and Arduino software. These circuits can be easily applied as an automatic irrigation system for small farms, gardens, or nurseries with improved efficiency and at reduced costs.
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) recently collaborated with corporate partners such as Esri and Microsoft to introduce Agricultural Research Service that integrates AI and IoT in data-driven farming. The new smart farming systems developed by the USDA include IoT-enabled farming equipment, drones, and deployed sensors which can give farmers real-time data on dynamic farming conditions.

















