Previously we have learned to control GPIO of Raspberry pi using two IoT platforms: IFTTT and Blynk App. In this project we explore another IOT cloud platform Adafuit IO. In this DIY tutorial we will control LED with Adafruit IO dashboard and Raspberry pi. Adafruit IO is a cloud service using which you can upload, display and monitor your data over the internet, and make your project IoT enabled. To test and try with some limitations, Adafruit IO is free to use.
Components Required
- Raspberry Pi
- LED
- Breadboard
- Resistor (250 ohm)
- Jumper Wires
- Adafruit IO
Circuit Diagram
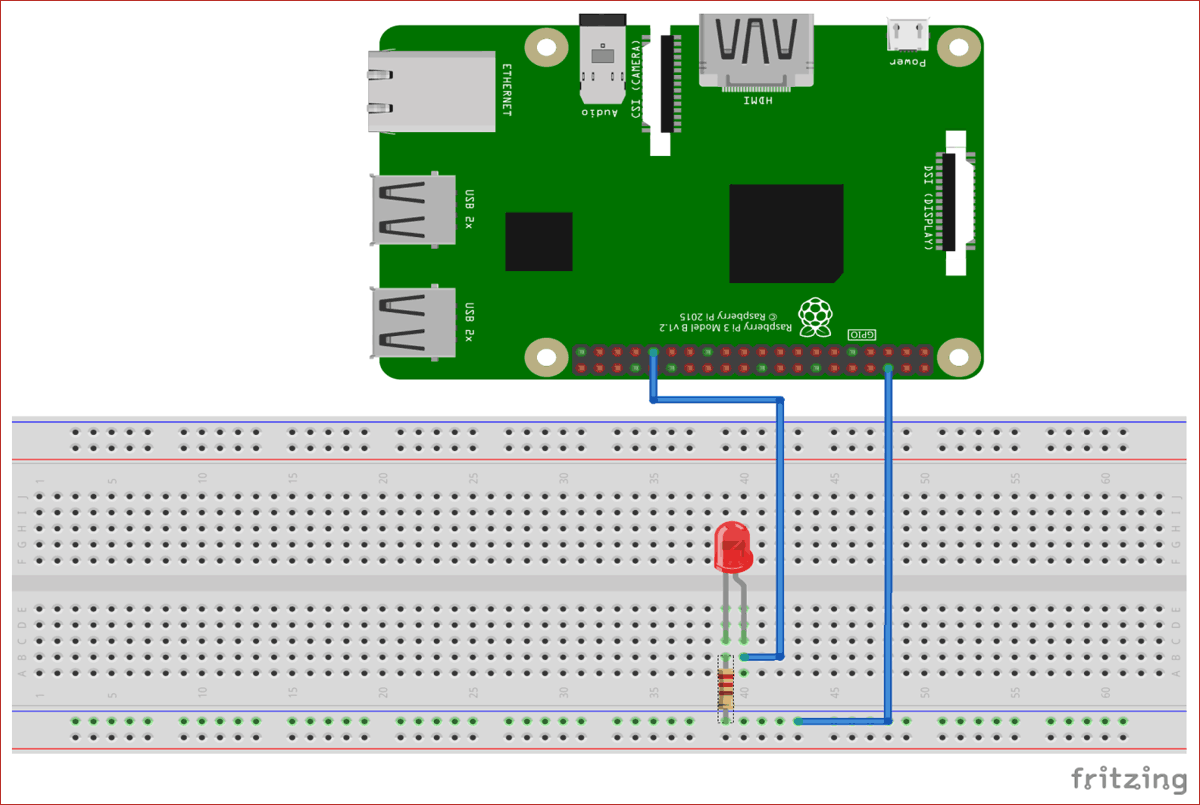
Connections of this project are very simple. Connect LED’s positive pin to Raspberry Pi’s 31st (GPIO6) pin and negative pin to resistor. Other part of the resistor is connected with ground pin of Raspberry Pi.
Step 1 Adafruit IO Setup for Raspberry Pi GPIO control
1. For Adafruit IO setup the first thing you will need to do is to sign up to Adafruit IO. To sign up go to Adafruit IO’s site https://io.adafruit.com and click on ‘Get started for Free’ on top right of the screen.

2. After this a window will pop up where you need to fill your details
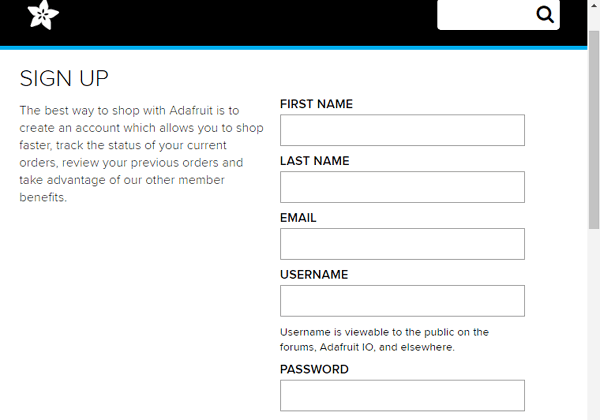
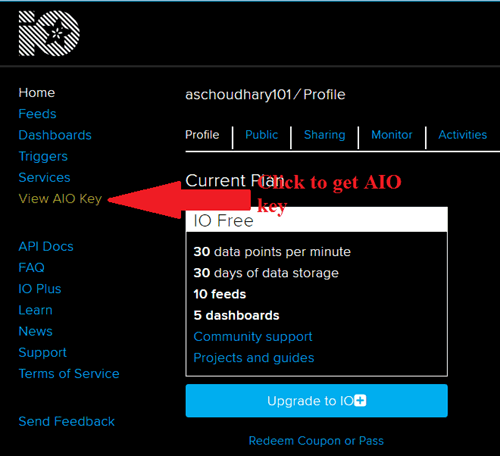
In sign up window fill your details like: your name, mail id, username etc. Then click on save settings and your account is created. To get your AIO key click on ‘View AIO Key’.
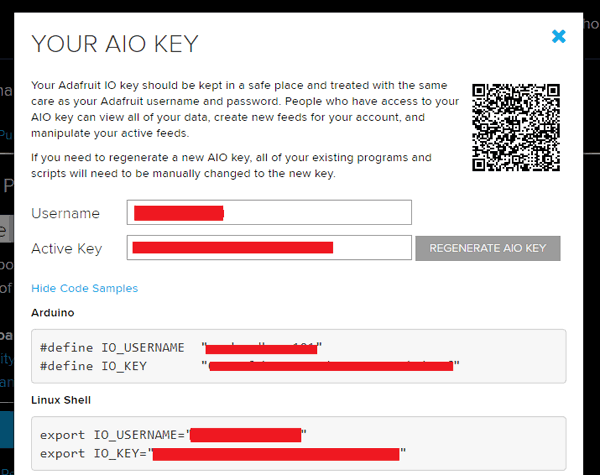
3. A window will pop up with your Adafruit IO AIO Key. Copy this key you'll need it later in your python code.
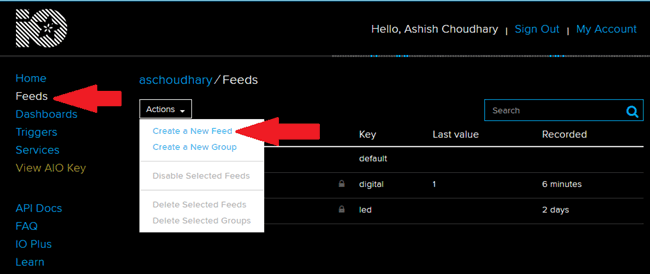
4. Now after this you need to create a feed. To create a feed click on ‘Feed’. Then click on ‘Actions’, you will see some options from them click on ‘Create a New Feed’.
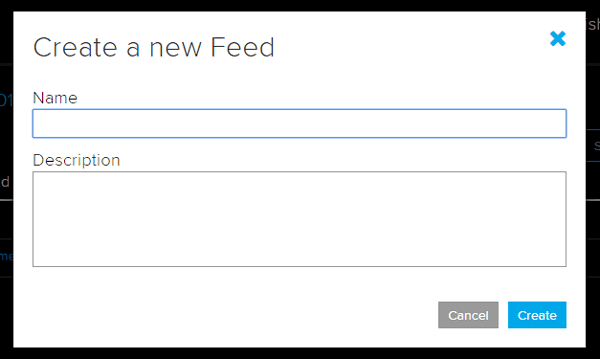
5. After this a new window will open where you need to input:
Name – In name option write a short descriptive name of your feed. You can use Letters, numbers, and spaces.
Description - A long form description of your data. This field is not required, but you can write a description about your data.
6. Click on ‘Create’, you will then be redirected to your new feed.
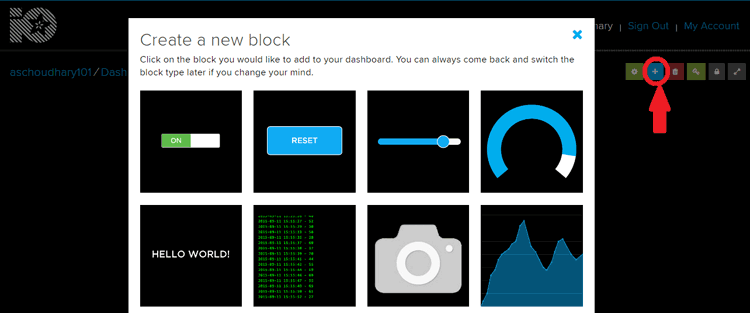
7. Next, to add a new Toggle Block you need to create a dashboard. Creating a Dashboard is same as Feed. So follow the same steps. Now to add block click on ‘Plus sign’ on top right corner of the screen and click on first option.
8. Name the block whatever you like, and set On Text to a value of 1 and Off Text to a value of 0. Make sure you have selected the Digital feed as the data source for the toggle.
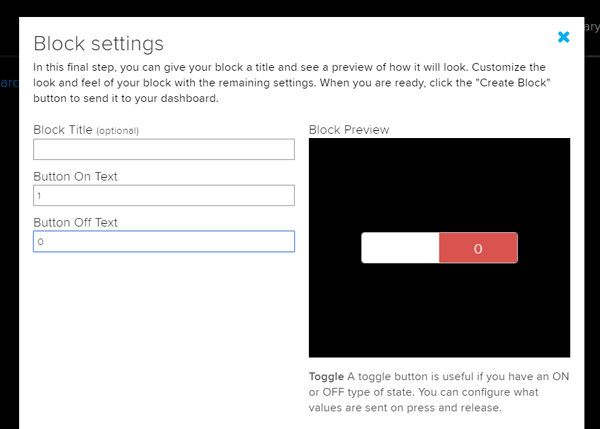
9. When you finished click on ‘Create Block’ to create your block.
Step 2 Raspberry Pi Setup for Adafruit IO
First update your Raspberry Pi using below commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
And
sudo pip3 install --upgrade setuptools
Now install the Raspberry Pi GPIO library
pip3 install RPI.GPIO
Install Adafruit Blinka library using this command:
pip3 install adafruit-blinka
Then using the following command install the Adafruit IO library
pip3 install adafruit-io
Now, download the adafruit/io-client-python repository by using:
git clone https://github.com/adafruit/io-client-python.git
Now go to the examples folder using:
cd io-client-python/examples/basics/
Now make a file using
sudo nano led.py
then copy paste the python code in this file and run the program using below command:
python3 led.py
Python Code
Complete python for this project is given at the end of this tutorial.
If your code runs successfully you will see the following in the terminal of your Pi.
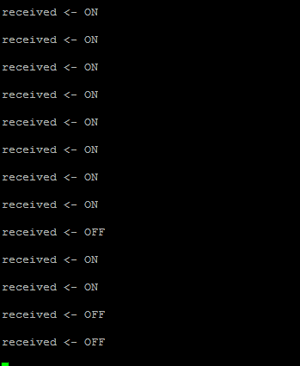
Toggle the button on your Adafruit IO dashboard to change the Led state.

So it’s very easy to integrate Adafruit IO in your IoT projects. Also check our other similar tutorials with other popular IoT cloud platforms:
IoT Controlled LED with Blynk App and Raspberry Pi
How to Control an LED with Raspberry Pi Webserver using Apache
import time
import digitalio
import board
from Adafruit_IO import Client, Feed, RequestError
ADAFRUIT_IO_KEY = 'your APIO KEY' # Set your APIO Key
# Set to your Adafruit IO username.
ADAFRUIT_IO_USERNAME = 'Your Username'
aio = Client(ADAFRUIT_IO_USERNAME, ADAFRUIT_IO_KEY)
try:
digital = aio.feeds('LED')
except RequestError:
feed = Feed(name="LED")
LED = aio.create_feed(feed)
# led set up
led = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.D6)
led.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
while True:
data = aio.receive(digital.key)
if int(data.value) == 1:
print('received <- ON\n')
elif int(data.value) == 0:
print('received <- OFF\n')
led.value = int(data.value)